The world of analytics is constantly evolving, and Google Analytics has been at the forefront of helping businesses gain valuable insights into their online performance. With the recent release of Google Analytics 4 (GA4), many are left wondering about the differences between this new version and its predecessor, Universal Analytics. In this article, we will explore the key features and functionality of both Universal Analytics and Google Analytics 4, compare their data collection methods and reporting capabilities, and analyze the considerations for transitioning from one to the other. By the end, you will have a better understanding of which analytics platform may be better suited to meet your business needs and goals.
Understanding the Evolution of Google Analytics
Google Analytics has come a long way since its inception in 2005. Back in the day, it offered a simple yet effective way to track website visits and gain insights into user behavior. Fast forward to today, and the latest iteration of Google Analytics has emerged – Google Analytics 4. This new version introduces several updates and enhancements to the way data is collected and analyzed, promising a more comprehensive and insightful view of user interactions.
Some Key Features and Functionality of Universal Analytics and Google Analytics 4
Let’s start by getting familiar with Universal Analytics, the tried-and-true version that has been the go-to choice for many businesses. Universal Analytics uses JavaScript tracking code placed on web pages to collect data about user interactions. It tracks various metrics like page views, sessions, bounce rates, and conversions, among others. This data is then sent to the Google Analytics servers for analysis and reporting.
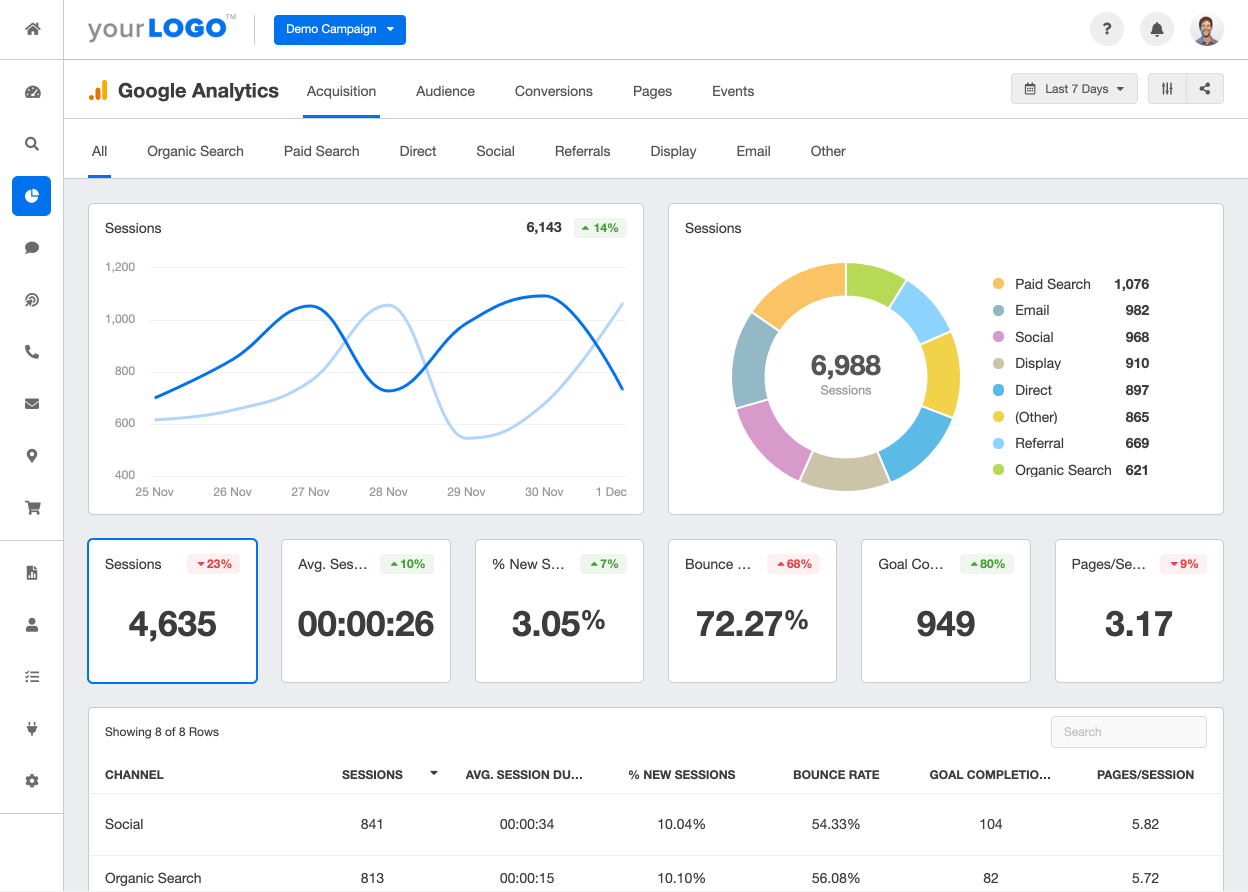
One of the standout features of Universal Analytics is its flexibility. Businesses can customize and track specific events and interactions on their websites using event tracking, e-commerce tracking, and enhanced link attribution. This level of customization allows for detailed analysis and optimization of user journeys. When it comes to reporting and analysis, Universal Analytics provides a wide array of reports and data visualization options. Its user-friendly interface makes it easy to navigate through various metrics and dimensions, enabling businesses to gain insights into user behavior, traffic sources, and conversion funnels.
Now, let’s turn our attention to Google Analytics 4, the shiny new version that promises to take data analysis to the next level. Unlike Universal Analytics, which relies heavily on JavaScript tracking code, Google Analytics 4 leverages a more flexible and future-proof data collection method called “Firebase,” which operates via an SDK (Software Development Kit). Firebase allows for enhanced data collection across multiple platforms, including websites, mobile apps, and even offline interactions. This means businesses can gain a more holistic view of user interactions and track performance across different touchpoints.
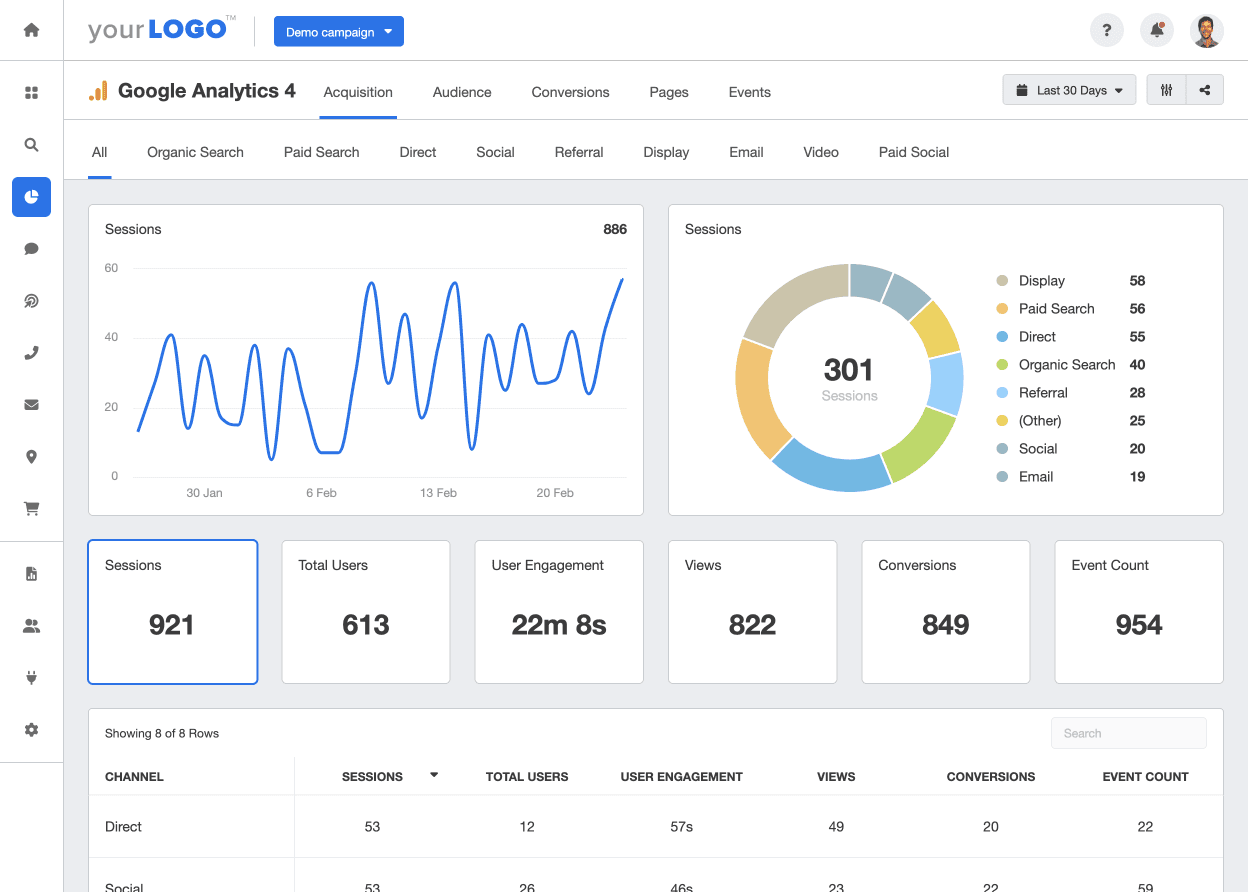
In terms of reporting and analysis features, Google Analytics 4 introduces some exciting new capabilities. It offers a more simplified and streamlined interface with machine learning at its core. You can discover trends, predict future outcomes, and even create custom metrics using the Analysis Hub. This empowers businesses to uncover valuable insights and make data-driven decisions.
Now that we have a basic understanding of both Universal Analytics and Google Analytics 4, let’s compare their data collection methods and assess their impact on data accuracy and integrity.
Universal Analytics relies on JavaScript tracking code, which can sometimes be affected by ad blockers or privacy settings. While it has been a reliable method for years, it may encounter limitations in tracking certain interactions or accurately measuring cross-platform usage.
On the other hand, Google Analytics 4’s Firebase data collection method offers more flexibility and robustness. By utilizing SDKs, it can capture data from a wide range of platforms, ensuring a more comprehensive view of user behavior. This approach provides businesses with a more accurate and complete understanding of their audience.
In terms of data accuracy and integrity, Google Analytics 4 holds an advantage due to its ability to track users across different devices and platforms. This helps businesses overcome the limitations of traditional cookie-based tracking and ensures a more accurate representation of user journeys.
In conclusion, while Universal Analytics has been a reliable tool for quite some time, Google Analytics 4 brings exciting new features and enhanced data collection methods to the table. Businesses looking for a more comprehensive view of user interactions and accurate data insights may find Google Analytics 4 to be the better choice. But hey, don’t just take my word for it – dive in, explore, and see which one suits your needs best!
Advantages and Limitations of Universal Analytics
Universal Analytics has been the go-to analytics platform for many businesses for years. Its advantages include a mature ecosystem of plugins and integrations, flexibility in customization, and familiarity among marketers and analytics professionals. It offers a wide range of reporting and analysis capabilities that suit the needs of different businesses.
However, Universal Analytics has its limitations, such as its reliance on pageviews and sessions as core metrics, less advanced analysis techniques, and challenges in tracking cross-device interactions accurately. As technology and user behavior evolve, these limitations can hinder businesses from gaining a comprehensive understanding of their audience.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Google Analytics 4
Google Analytics 4 has several benefits that make it an attractive option for businesses. Its advanced analysis techniques, machine learning capabilities, and user-centric data model provide deeper insights into user behaviour. The new reporting interface is more intuitive and offers increased flexibility. Furthermore, Google Analytics 4 is designed to adapt to the changing landscape of privacy regulations and cookie restrictions.
However, Google Analytics 4 is still in its early stages, and its ecosystem of plugins and integrations is not as robust as Universal Analytics. Additionally, transitioning to Google Analytics 4 may require significant adjustments in tracking implementation and analysis processes.